B058-SpringBoot
作者:小教学发布时间:2023-09-30分类:程序开发学习浏览:212
目录
- springboot
- 概念与作用
- 入门案例
- springboot运行方式
- 热部署
- 配置文件
- Profile多环境支持
- 整合测试-springboot-test
- Springboot-web
- 1.返回json数据
- 2.返回页面(模板技术)thymeleaf
- 1.导入thymeleaf依赖
- 2.模板文件
- 3.controller
- 4.启动类
- SSM整合
- 1.导包
- 2.项目目录结构+配置文件+扫描注解
- 3.测试
- 事务的传播机制
springboot
概念与作用
springboot是为 spring服务的,为简化Spring项目配置而生
它使用maven的方式对Spring应用开发进行进一步封装和简化
是用来简化spring应用搭建,开发,部署,监控的开发工具
简化Spring应用的搭建,开发,部署,监控的开发工具
简单的说,它使用maven的方式对Spring应用开发进行进一步封装和简化。
提供自动化配置
使编码更简单,使配置更简单,使部署更简单,使监控更简单
入门案例
创建Maven父项目和子项目
导入Spring Boot依赖
父节点添加parent依赖管理 子节点添加spring-boot-starter-web依赖
编码测试
新建一个Controller类
新建启动类
浏览器测试代码运行
<!--
groupId:打包后放到本地仓库的路径
artifactID:模块ID,同项目名
-->
<groupId>cn.itsource</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-parent</artifactId>
<!--打包
jar/war:将当前项目打包成jar或者war
pom:代表当前项目是父项目,不写任何java代码,只用来管理子项目和插件
maven-plugin:将当前项目打包成maven插件(牛)
-->
<packaging>pom</packaging>
父子项目在pom.xml文件的互相定位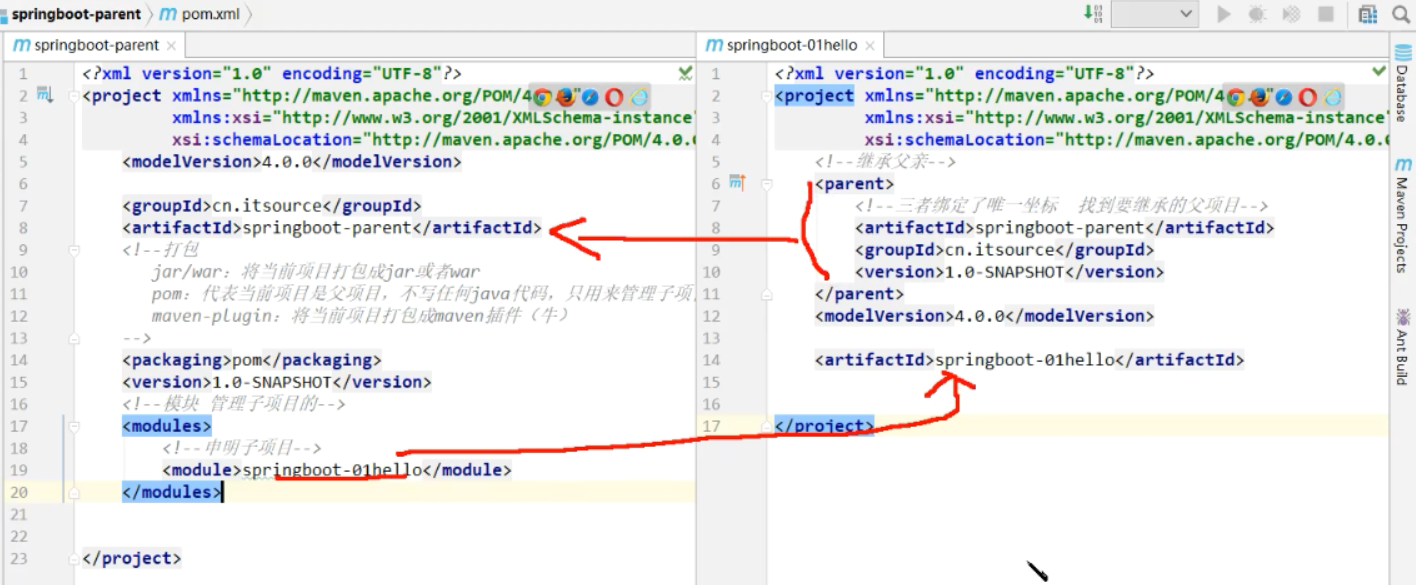
springboot运行方式
1.直接点击main方法
2.使用插件运行
3.打包运行
配置打包依赖 用package命令 到jar包所在路径cmd打开黑窗口 运行jar
热部署
1.添加依赖
2.启动项目
3.改代码
4.重新编译(关键)
配置文件
application.yml
application.properties (首选)
1.有了properties 可以存在yml吗? 可以存在
2.如果同时存在,我该用谁? 优先用properties,但是可以同时使用不一样的配置
yml(推荐)
冒号
空格 回车/换行 缩进/tab (最后一个值,只需要空格)
Profile多环境支持
1.多文档块 (不推荐使用)
将所有的环境配置写到一个yml中,通过—(必须是三个横杆)做分隔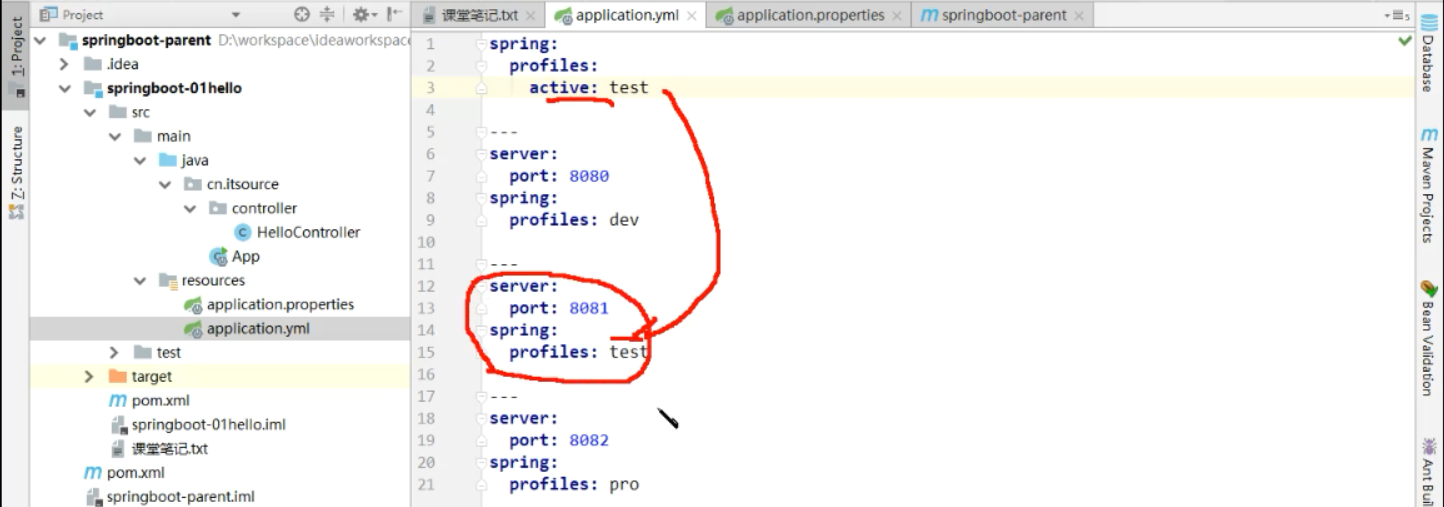
2.多文件方式
application-环境名.yml active表示生效环境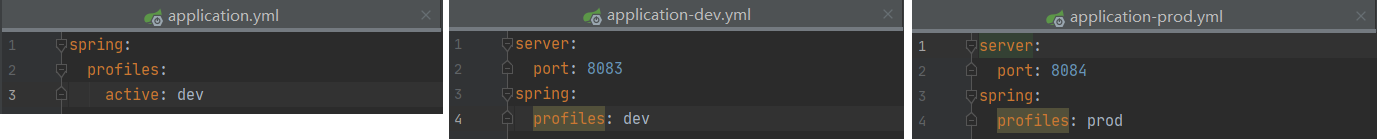
整合测试-springboot-test
1.基本测试 junit
2.基于Spring的测试
在测试类加注解
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
3.SpringBoot测试 - 使用流程
导对应包/依赖 引入测试依赖包
MyBean @Component
启动类 @SpringBootApplication psvm SpringApplication
测试类 @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest(classes = App.class)
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = TestApp.class)
public class TestSpringBoot {
@Autowired
MyBean myBean;
@Test
public void testHello(){
System.out.println(myBean);
}
}
Springboot-web
1.返回json数据
如我们的controller中的所有方法,返回的都是json格式
那么请你使用:@RestController === @Controller + @ResponseBody
2.返回页面(模板技术)thymeleaf
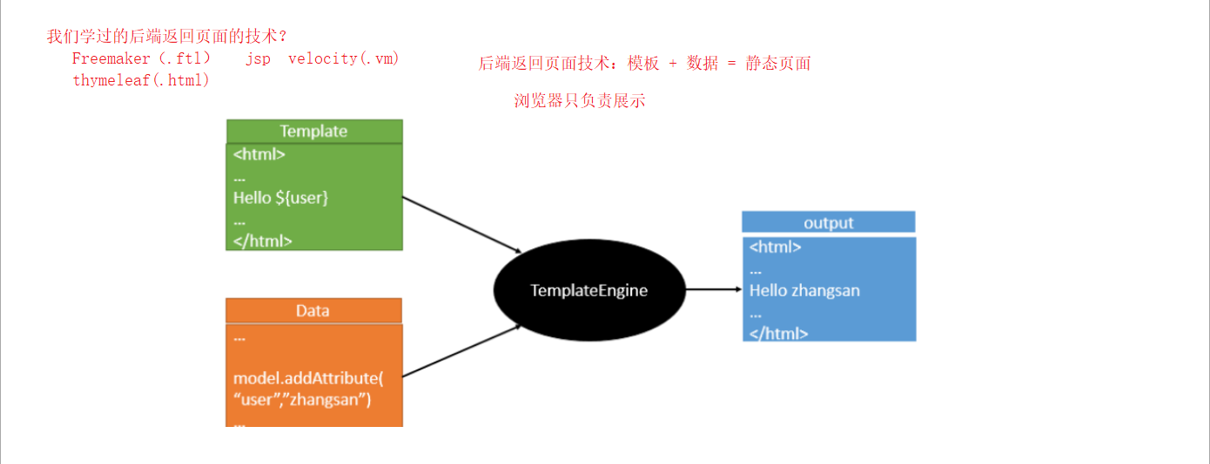
1.导入thymeleaf依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.模板文件
页面引入thymeleaf命名空间以支持th属性,使用th属性获取来自controller里model的数据
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>aaa</title>
</head>
<body>
<div th:text="${msg}">你好大兄弟</div>
</body>
</html>
3.controller
后端用model往页面添加数据,返回页面
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/thy")
public class ThyController {
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String toIndex(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg", "你好,thymeleaf!!!");
return "hello";//页面路径/名称
}
}
因为thymeleaf是页面,需要放置到资源文件中,SpringBoot的默认配置会到resources/templates/找模板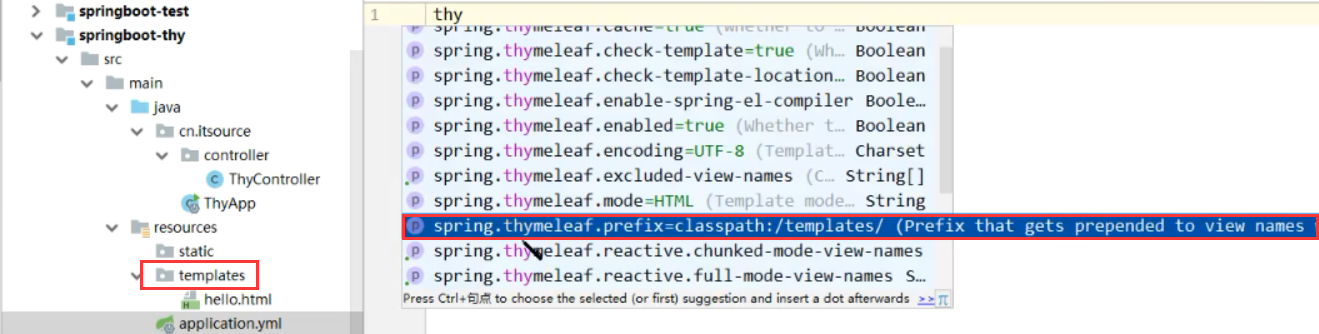
4.启动类
SSM整合
1.导包
导入mybatis核心包(mysql+jdbc)、Mybatis提供的SpringBoot依赖包、SpringBoot测试包
<dependencies>
<!-- mysql 数据库驱动. -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--Mybatis提供的SpringBoot依赖包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2.项目目录结构+配置文件+扫描注解
项目目录结构 domain query mapper service controller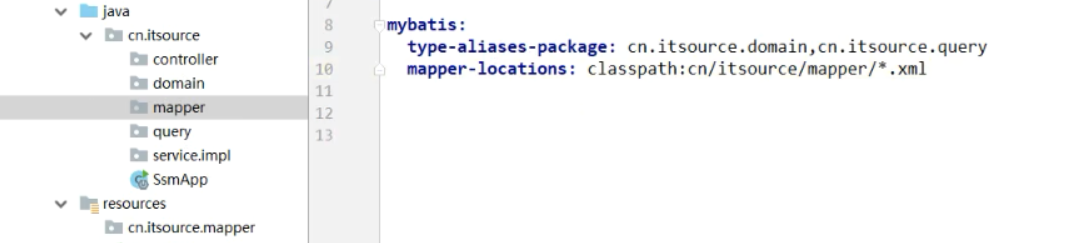
核心配置文件yml (数据源四大金刚 扫描别名和扫描文件路径)
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql:///mybatis
username: root
password: root
mybatis:
type-aliases-package: cn.itsource.domain,cn.itsource.query # 可免除实体类@Component注解
mapper-locations: classpath:cn/itsource/mapper/*.xml
启动类加@MapperScan扫描
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("cn.itsource.mapper")
public class SsmApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SsmApp.class,args);
}
}
3.测试
表&实体 -> mapper接口+xml实现 -> service -> test -> controller
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = SsmApp.class)
public class TestProduct {
@Autowired
ProductServiceImpl productService;
@Test
public void test(){
productService.loadAll().forEach(a->{
System.out.println(a);
});
}
@Test
public void testSave(){
Product product = new Product("测试数据");
productService.save(product);
}
}
注意resource包下不能一次直接建多层包
事务的传播机制
一组操作同时成功或者同时失败
@Override
@Transactional
public void save(Product product) {
productMapper.save(product);
//int i=1/0;
}
只读事务 —加到查询上面
@Transactional(readOnly = true, propagation = Propagation.SUPPORTS)
public List<Product> loadAll() {
return productMapper.loadAll();
}
类与方法上同时存在的注解使用哪个?就近原则
@Service
@Transactional(readOnly = true, propagation = Propagation.SUPPORTS)
public class ProductServiceImpl implements IProductService {
@Autowired
ProductMapper productMapper;
@Override
@Transactional // 后面不写等同于@Transactional(readOnly = false, propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void save(Product product) {
productMapper.save(product);
//int i=1/0;
}
@Override
public List<Product> loadAll() {
return productMapper.loadAll();
}
}
一个方法里只能有一个事务
事务的传播机制:
REQUIRED:支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,则新建一个事务(默认)
SUPPORTS:支持当前事务,当前当前没有事务,就不加事务
REQUIRES_NEW:新建事务,如果当前有事务,则把事务挂起,等着我先执行完成
NEVER: 不支持事务,如果当前有事务,则抛出异常
事务传播机制的作用:用来保证一组操作只有一个事务,解决事务冲突。
@Options(useGeneratedKeys = true, keyProperty = “id”, keyColumn = “id”)
@Insert(“insert into Demo(name,password) values(#{name},#{password})”)
public long save(Demo name);//对象上面也有
- 程序开发学习排行
- 最近发表


