Pytorch Advanced(三) Neural Style Transfer
作者:小教学发布时间:2023-09-26分类:程序开发学习浏览:224
导读:神经风格迁移在之前的博客中已经用keras实现过了,比较复杂,keras版本。这里用pytorch重新实现一次,原理图如下:from__future__import...
神经风格迁移在之前的博客中已经用keras实现过了,比较复杂,keras版本。
这里用pytorch重新实现一次,原理图如下:
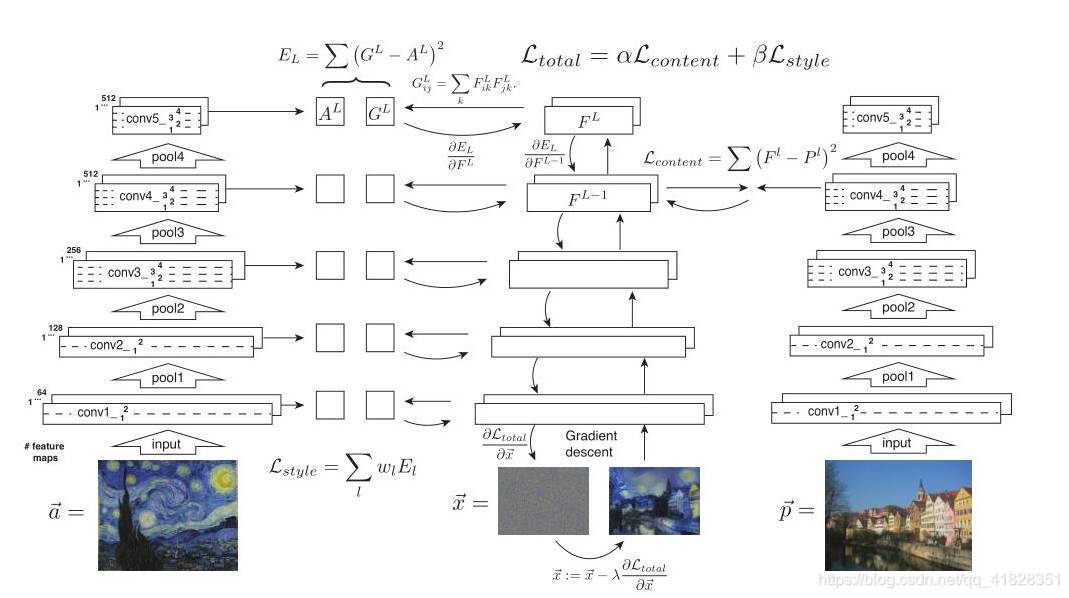
from __future__ import division
from torchvision import models
from torchvision import transforms
from PIL import Image
import argparse
import torch
import torchvision
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')加载图像
def load_image(image_path, transform=None, max_size=None, shape=None):
"""Load an image and convert it to a torch tensor."""
image = Image.open(image_path)
if max_size:
scale = max_size / max(image.size)
size = np.array(image.size) * scale
image = image.resize(size.astype(int), Image.ANTIALIAS)
if shape:
image = image.resize(shape, Image.LANCZOS)
if transform:
image = transform(image).unsqueeze(0)
return image.to(device)这里用的模型是 VGG-19,所要用的是网络中的5个卷积层
class VGGNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
"""Select conv1_1 ~ conv5_1 activation maps."""
super(VGGNet, self).__init__()
self.select = ['0', '5', '10', '19', '28']
self.vgg = models.vgg19(pretrained=True).features
def forward(self, x):
"""Extract multiple convolutional feature maps."""
features = []
for name, layer in self.vgg._modules.items():
x = layer(x)
if name in self.select:
features.append(x)
return features模型结构如下,可以看到使用序列模型来写的VGG-NET,所以标号即层号,我们要保存的是['0', '5', '10', '19', '28'] 的输出结果。
VGG(
(features): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): ReLU(inplace)
(2): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(3): ReLU(inplace)
(4): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(5): Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(6): ReLU(inplace)
(7): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(8): ReLU(inplace)
(9): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(10): Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(11): ReLU(inplace)
(12): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(13): ReLU(inplace)
(14): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(15): ReLU(inplace)
(16): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(17): ReLU(inplace)
(18): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(19): Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(20): ReLU(inplace)
(21): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(22): ReLU(inplace)
(23): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(24): ReLU(inplace)
(25): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(26): ReLU(inplace)
(27): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(28): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(29): ReLU(inplace)
(30): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(31): ReLU(inplace)
(32): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(33): ReLU(inplace)
(34): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(35): ReLU(inplace)
(36): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(avgpool): AdaptiveAvgPool2d(output_size=(7, 7))
(classifier): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=25088, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(1): ReLU(inplace)
(2): Dropout(p=0.5)
(3): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(4): ReLU(inplace)
(5): Dropout(p=0.5)
(6): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=1000, bias=True)
)
)训练:
接下来对训练过程进行解释:
1、加载风格图像和内容图像,我们在之前的博客中使用的一幅加噪图进行训练,这里是用的内容图像的拷贝。
2、我们需要优化的就是作为目标的内容图像拷贝,可以看到target需要求导。
3、VGGnet参数是不需要优化的,所以设置为验证状态。
4、将3幅图像输入网络,得到总共15个输出(每个图像有5层的输出)
5、内容损失:这里是遍历5个层的输出来计算损失,而在keras版本中只用了第4层的输出计算损失
6、风格损失:同样计算格拉姆风格矩阵,将每一层的风格损失叠加,得到总的风格损失,计算公式同样和keras版本有所不一样
7、反向传播
def main(config):
# Image preprocessing
# VGGNet was trained on ImageNet where images are normalized by mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406] and std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225].
# We use the same normalization statistics here.
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.485, 0.456, 0.406),
std=(0.229, 0.224, 0.225))])
# Load content and style images
# Make the style image same size as the content image
content = load_image(config.content, transform, max_size=config.max_size)
style = load_image(config.style, transform, shape=[content.size(2), content.size(3)])
# Initialize a target image with the content image
target = content.clone().requires_grad_(True)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam([target], lr=config.lr, betas=[0.5, 0.999])
vgg = VGGNet().to(device).eval()
for step in range(config.total_step):
# Extract multiple(5) conv feature vectors
target_features = vgg(target)
content_features = vgg(content)
style_features = vgg(style)
style_loss = 0
content_loss = 0
for f1, f2, f3 in zip(target_features, content_features, style_features):
# Compute content loss with target and content images
content_loss += torch.mean((f1 - f2)**2)
# Reshape convolutional feature maps
_, c, h, w = f1.size()
f1 = f1.view(c, h * w)
f3 = f3.view(c, h * w)
# Compute gram matrix
f1 = torch.mm(f1, f1.t())
f3 = torch.mm(f3, f3.t())
# Compute style loss with target and style images
style_loss += torch.mean((f1 - f3)**2) / (c * h * w)
# Compute total loss, backprop and optimize
loss = content_loss + config.style_weight * style_loss
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if (step+1) % config.log_step == 0:
print ('Step [{}/{}], Content Loss: {:.4f}, Style Loss: {:.4f}'
.format(step+1, config.total_step, content_loss.item(), style_loss.item()))
if (step+1) % config.sample_step == 0:
# Save the generated image
denorm = transforms.Normalize((-2.12, -2.04, -1.80), (4.37, 4.46, 4.44))
img = target.clone().squeeze()
img = denorm(img).clamp_(0, 1)
torchvision.utils.save_image(img, 'output-{}.png'.format(step+1))写在if __name__=="__main__"后面的语句只会在本脚本中才能被执行,被调用时是不会被执行的。
python的命令行工具:argparse,很优雅的添加参数
但是由于jupyter不支持添加外部参数,所以使用了外部博客的方法来支持(记住更改读取图片的位置)
import sys
if __name__ == "__main__":
#解决方案来自于博客
if '-f' in sys.argv:
sys.argv.remove('-f')
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--content', type=str, default='png/content.png')
parser.add_argument('--style', type=str, default='png/style.png')
parser.add_argument('--max_size', type=int, default=400)
parser.add_argument('--total_step', type=int, default=2000)
parser.add_argument('--log_step', type=int, default=10)
parser.add_argument('--sample_step', type=int, default=500)
parser.add_argument('--style_weight', type=float, default=100)
parser.add_argument('--lr', type=float, default=0.003)
#config = parser.parse_args()
config = parser.parse_known_args()[0] #参考博客 https://blog.csdn.net/ken_for_learning/article/details/89675904
print(config)
main(config)- 程序开发学习排行
- 最近发表


